
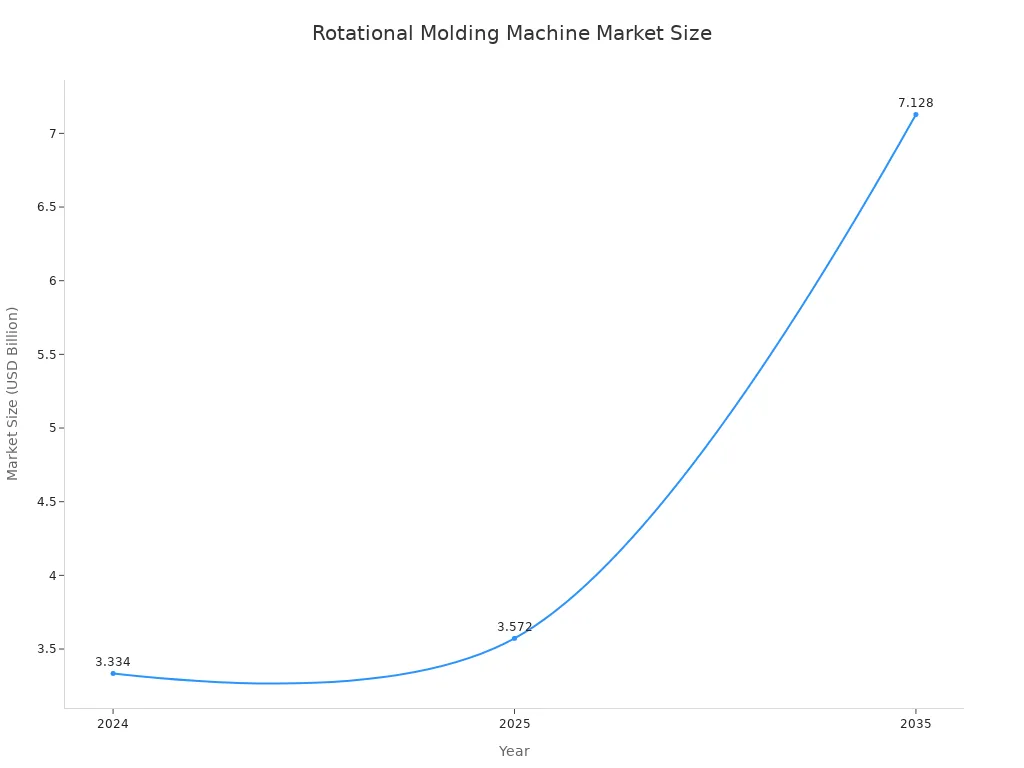
Rotational Molding is a prevalent manufacturing process. It forms hollow plastic products through heat and biaxial rotation. This method creates countless everyday items. The global rotomolding market reached $1.90 billion in 2024, projecting $3.03 billion by 2032. The market for rotational molding machines also shows robust growth. Rotational Molding Molds are essential for this industry’s expansion.
| Segment | 2024 (USD Billion) | 2032 (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| Global Rotomolding Market | 1.90 | 3.03 |
Key Takeaways
- Rotational molding makes strong, hollow plastic products. It uses heat and rotation to form items like toys and tanks.
- This method is good for making large items. It also costs less for molds than other ways to make plastic products.
- Rotational molding creates products with no seams. This makes them very durable and useful for many things, from kayaks to storage tanks.
Understanding the Rotational Molding Molds ProcessHow Rotational Molding Works
Rotational molding, often called rotomolding, is a manufacturing process that creates hollow, seamless plastic products. It involves a specific sequence of steps to achieve the desired product.
- Mold Preparation: Manufacturers first fill the hollow mold with a precise amount of polymer powder or resin. They also add pre-compounds for color and hardness. A mold release agent is applied to the mold’s interior. The mold is then preheated, closed, and moved into an oven.
- Mold Heating: Inside the oven, the mold rotates simultaneously on two axes. This biaxial rotation ensures the material spreads evenly across the mold’s interior surfaces. The rotation speed remains low to prevent centrifugal forces from affecting material distribution. Proper timing is essential during this stage. It ensures complete melting and adherence of the material without degrading its mechanical properties.
- Mold Cooling: After heating, the mold moves into a cooling chamber. It cools using air, water spray, or a combination of both, while still rotating. Careful control of the cooling rate is vital. This prevents issues such as shrinkage, warping from rapid cooling, or inconsistent wall thicknesses from slow cooling. Software often helps optimize these cooling rates.
- Mold Unloading: The final step involves carefully removing the molded part from the mold. The effectiveness of the mold release agent applied earlier and proper mold design are critical. They prevent damage to the part and ensure high-quality products.
The primary material used in rotational molding is polyethylene (PE). This includes Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE), High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE), and Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). LLDPE is the most common type, offering a range of stiffness for various applications. HDPE provides greater rigidity, surface hardness, and chemical resistance, making it ideal for large tanks. LDPE is flexible and lightweight, suitable for food-safe applications. Other polymers like Polypropylene (PP) are also used. PP offers a high melting point and resistance to various chemicals, finding use in toys and packaging.
Key Advantages of Rotational Molding Molds
Rotational molding offers distinct advantages, especially when compared to other plastic manufacturing methods like injection molding. These benefits make it a preferred choice for many products.
Rotational molding excels at producing larger parts. It accommodates significantly larger items than injection molding. This allows for the creation of products such as storage tanks, playground equipment, and large furniture pieces. The process ensures uniform material distribution, leading to products with high strength and durability. These robust products endure harsh conditions over time.
The cost-effectiveness of tooling is another significant advantage. Rotational Molding Molds are generally less expensive than injection molding molds. They can be approximately one-tenth the cost. This makes Rotational Molding Molds a more economical choice for smaller production runs or projects requiring frequent design modifications. The durability of these molds further contributes to long-term cost savings.
Rotational molding also provides design flexibility. It allows for complex shapes and undercuts without incurring additional tooling expenses. This method handles large, complex shapes with ease. The process results in seamless, one-piece hollow objects. Manufacturers can further enhance these objects with foam filling for structural integrity and insulation. This seamless construction eliminates the need for welding or assembly, reducing manufacturing steps and potential failure points.
For low-volume production runs, rotational molding proves particularly cost-effective. It is well-suited for specialized or custom-made products. Unlike injection molding, which requires high-volume production to offset expensive tooling, rotational molding provides an economical option for smaller quantities, often fewer than 3,000 units per year. The primary material, polyethylene resin powder, is relatively inexpensive. The process also minimizes material waste, as excess material can be recycled and reused, further reducing costs.
Everyday Products Shaped by Rotational Molding Molds

Rotational molding shapes a vast array of products that people encounter daily, from household items to industrial equipment. This versatile manufacturing process creates durable and functional goods across various sectors.
Consumer Goods and Home Essentials
Rotational molding produces many common consumer goods and home essentials. People often see playground equipment, balls, and children’s toys made using this method. Outdoor furniture, garden planters, rain barrels, and even decorative yard flamingos also come from rotational molding. This process also creates plastic toys, decorative items, and baby cribs.
Specific household items frequently benefit from rotational molding. Ice boxes, for example, offer high insulation and durability for cold storage and transport. Dustbins are impact-resistant, weatherproof, and seamless, ensuring leak-free use and easy cleaning for effective waste collection. Other items include pet houses, bins, refuse containers, and doll parts. Manufacturers even produce underground cellars for vine and vegetable storage with this method. Baby cribs and changing stations are lighter, sturdy, and feature seamless designs for easy cleaning, often including integrated storage. Industrial bins and recycling units also use seamless plastic for easy cleaning and strong double-walled designs to prevent cracks or leaks.
Rotational molding is particularly suitable for children’s toys due to specific material properties. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) offers versatility, allowing for extremely solid or flexible profiles, ideal for various toy designs, including inflatable toys. Rotomolded toys inherently provide greater resistance and durability compared to those made with other materials. This is crucial for items exposed to adverse weather conditions and frequent use by children. Safety is paramount; materials must be certified, non-toxic, and manufactured without sharp corners to ensure children’s safety and comply with legislation. Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) offers good durability and medium stiffness, making toys robust yet forgiving. When certified prime virgin LLDPE is used, it provides excellent resistance to chemicals and environmental stress cracking, ensuring longevity and safety. Manufacturers can enhance LLDPE with UV stabilizers, anti-microbials, anti-fungals, and pigments for various colors, improving the toy’s features. Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) is commonly recycled, aligning with environmental considerations for children’s products and is specifically used for toys.
Recreational and Outdoor Gear
Rotational molding plays a crucial role in creating recreational and outdoor gear. This includes playground equipment like slides and swing sets. Recreational watercraft such as kayaks, canoes, and boats also utilize this process. Ice rescue equipment, sporting goods, outdoor furniture, and camping and RV accessories are other examples. Urban furniture, pools, and coolers for camping also benefit from rotational molding.
Kayaks and canoes demonstrate the exceptional benefits of rotational molding. The process results in low residual stress and a one-piece construction with consistent wall thickness, making kayaks highly resistant to cracking or bending. This creates a smooth, seamless design, eliminating sharp corners for a sleek finish, reducing drag, and enhancing safety. Color is embedded within the plastic during molding, preventing chipping, scratching, or fading. UV-stabilized polyethylene maintains vibrancy over time. Molded-in brass inserts provide durable fixings for components, contributing to superior structural integrity and corrosion resistance. The manufacturing process also minimizes waste and utilizes recyclable materials, making it eco-friendly. These kayaks, made of high-density polyethylene, are known for strength and resistance to impact and UV rays, ensuring longevity. They feature a low center of gravity and wide hull, providing excellent stability, ideal for beginners. Their lightweight nature makes them easy to transport and requires minimal upkeep, offering a low-maintenance and user-friendly experience.
Industrial and Specialized Applications
Rotational molding extends its utility to various industrial and specialized applications. Plastic tanks and containers are widely used for water storage, septic tanks, oil tanks, and chemical storage. Their seamless, hollow form makes them durable and resistant to impact and weathering, suitable for outdoor and industrial use. Medical equipment also utilizes rotational molding for prosthetics, medical cases, and medical waste containers. The seamless, hollow design facilitates easy cleaning and sterilization, ensuring a sanitary environment. Large storage tanks and containers are essential for industrial and agricultural sectors to store water, chemicals, and fertilizers. Their seamless design minimizes leaks and contamination. The ability to produce large, custom sizes economically makes rotational molding a preferred choice. Medical and healthcare devices increasingly use this process for sterilization containers, IV stands, and storage cases due to its ability to produce sterile, seamless, and durable components that meet strict regulatory standards.
Manufacturing large storage tanks with rotational molding offers significant advantages. It produces one-piece, seamless vessels, eliminating weld seams, which are potential leak points. A 6500-gallon steel tank, for instance, can have up to 70 yards of welded seams. Rotomolded Tanks feature homogenous, one-layer construction, preventing weak spots, wicking, or delamination common in fiberglass tanks. Engineers design sidewalls and the bottom knuckle radius for extra strength, maximizing thickness at critical stress points to handle hoop stress from stored chemicals.Seamless interiors prevent leakage and contamination, ensuring fluid retention. The enhanced mechanical strength from seamless construction eliminates weak points like welded seams, making containers stronger and more resistant to physical stress or impacts. The process streamlines mold setup compared to injection or blow molding, allowing for quicker turnaround times. It offers adaptability for various volume requirements, from small bottles to large vessels. Inherent shapes like cylindrical or spherical designs distribute stress evenly, enhancing overall structural integrity. Rotomolded plastic, often polyethylene, is UV-protected, rust-free, and corrosion-resistant, unlike metals, and thick walls enhance strength. The process releases no dangerous toxins, produces minimal waste, and plastics are 100% recyclable, minimizing environmental impact. The hot plastics conform to the mold, allowing for a wide range of designs and flexibility in producing items of different sizes. The lower mold cost for Rotational Molding Molds makes them suitable for prototypes and smaller production runs.
Why Rotational Molding Molds Excel for These Products

Unmatched Durability and Design Freedom
Rotational molding offers exceptional durability and extensive design freedom. This process allows for complex geometries in one-piece designs. Advanced CAD/CAM and CNC machining facilitate the creation of virtually any shape. Manufacturers can consolidate multiple components, like thermoformed or sheet metal parts, into a single, hollow plastic product. The stress-free nature of the process naturally builds material thickness in corners and ribs. This leads to inherently stronger products without material thinning in critical areas. Rotational molding also allows for undercuts and cored features, which are difficult or costly with blow molding. It also supports in-mold decorating and mold-in inserts.
Cost-Effectiveness for Complex Shapes
Rotational molding provides a cost-effective solution for complex shapes. It uses cheaper and simpler aluminum or sheet metal molds. This contrasts with blow molding, which requires expensive tooling. This makes rotational molding an economical choice, especially for designs requiring adjustments. The molten resin slowly coats the mold, allowing for superior design flexibility and various wall thicknesses. For small double-wall products, a maximum thickness variation of 0.5 to 0.75 mm is achievable. However, producing intricate designs may require longer cycle times, increasing labor costs due to less automation.
Seamless Construction and Material Versatility
Seamless construction is a significant advantage of rotational molding. This process creates one-piece products, eliminating weak points like welded seams. This enhances structural integrity and minimizes potential failure points. Products are mechanically stronger and better equipped to withstand physical stress or impacts. This is ideal for applications requiring durability and fluid retention without leakage or contamination. Rotational Molding Molds also accommodate a wide range of materials, primarily various types of polyethylene, offering versatility for different product requirements.
Rotational molding profoundly impacts modern product design, creating durable, seamless items. The process innovates manufacturing by minimizing waste, promoting material recyclability, and embracing advanced techniques like robotic rotational molding for enhanced precision. This continuous evolution ensures its vital role across diverse industries.
FAQ
What makes rotational molding molds cost-effective?
Rotational molding molds are generally less expensive than injection molding tools. This makes them ideal for smaller production runs or when designs require frequent modifications.
What materials does rotational molding primarily use?
Rotational molding mainly uses polyethylene (PE) in various forms like LLDPE, HDPE, and LDPE. Manufacturers also use other polymers such as polypropylene for specific product requirements.
Can rotational molding produce complex product shapes?
Absolutely! Rotational molding offers significant design freedom. It creates complex, hollow shapes and integrates features like undercuts or molded-in inserts into a single, seamless product.
Media Contact
Company Name: Ningbo Jinhong Mold CO., LTD.
Email: Send Email
Country: China
Website: https://www.jinhongmold.com/
